Back
Back
Introduction
Have you ever thought that there would be a technology where you can trade with any kind of person/company over the world? Definitely, it is Blockchain.
The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value. The Blockchain is a continuous chain which contains any kind of information in blocks where every block is connected to its previous and following blocks in the chain. This technique was originally described in 1991 by a group of researchers and was originally intended to time-stamp digital documents so that it’s not possible to backdate them or to tamper them. Almost like a notary.
For this we need a system where records could be stored, facts can be verified by anyone and security is guaranteed. That way no one could cheat the system by editing records because everyone using the system would be watching it. Systems like this are on the horizon and the software that powers them it's called a Blockchain.
About Blockchain
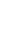
Blockchain stores the information across the network of personal computers making them not just decentralized but distributed.
This means no central company or person owns the system yet everyone can use it and help run it. This is important because it means it's difficult for any one person to take down the network or corrupt it. The people who run the system use their computer to hold bundles of records submitted by others known as "blocks " in a chronological chain. The Blockchain uses a form of math called cryptography to ensure that records can't be counterfeited or changed by anyone else.
How does it works?
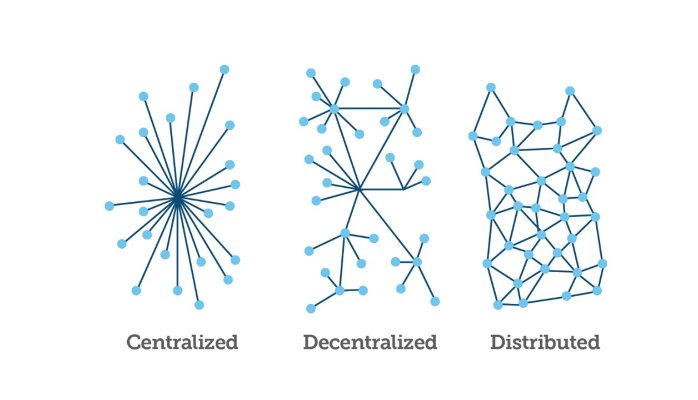
A blockchain is a distributed ledger that is completely open to anyone within the chain. It has an interesting property that is, once some data has been recorded inside a blockchain it becomes very difficult to change it. Blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called ’blocks,’ which are linked and secured using cryptography. Each block contains some data, hash of the present block and hash of the previous block. The data that is stored inside a block depends on the type of blockchain. Ex: Bitcoin.
Introduction of Blockchain with Bitcoin Over the Banks
Money exists to facilitate trade, throughout the centuries trade has become incredibly complex. Every one trades with everyone. Worldwide trade is recorded in bookkeeping. And this information is often closed and isolated to the public. For this reason, we used third parties and middleman we trust to facilitate and approve our transactions. Think of governments, banks, accountants, notaries and the paper money in our wallet. We call these trusted third parties. This brings us to the essence of Bitcoin. Bitcoin software enables a network of computers to maintain a collective bookkeeping via the internet. This bookkeeping is neither closed nor in-control of one party rather it is public and available in one digital ledger which is fully distributed across the network. We call this the blockchain.
Is Blockchain Secured?
Yes, in blockchain every block has a hash. You can compare a hash to a fingerprint. It identifies a block and all of its contents and it's always unique, just as a fingerprint. Once a block is created, it’s hash is being calculated. Changing something inside the block will cause the hash to change. So, in other words, hashes are very useful when you want to detect changes to blocks. If the fingerprint of a block changes, it is no longer the same block. The third element inside each block is the hash of the previous block. This effectively creates a chain of blocks and it is this technique that makes a blockchain so secure.
So, changing a single block will make all following blocks invalid. But using hashes is not enough to prevent tampering. Computers these days are very fast and can calculate hundreds of thousands of hashes per second. You could effectively tamper a block and recalculate all the hashes of other blocks to make your blockchain valid again. So to mitigate this, blockchains have something called proof-of-work. It's a mechanism that slows down the creation of new blocks.
Network Secure Connectivity:
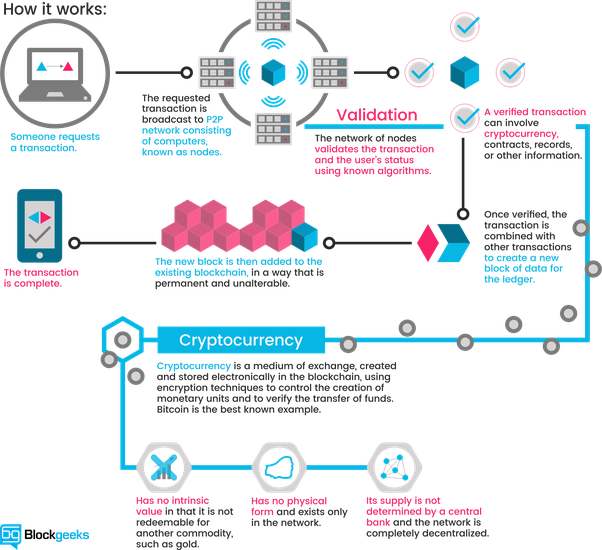
Blockchain mechanism makes it very hard to tamper with the blocks because if you tamper with one block you'll need to recalculate the proof-of-work for all the following blocks. So, the security of a blockchain comes from its creative use of hashing and the proof-of-work mechanism. But there is one more way that blockchains secure themselves and that's by being distributed. Instead of using a central entity to manage the chain, blockchains use a P2P(peer-to-peer) network and anyone is allowed to join. When someone joins this network, he gets the full copy of the blockchain. The node can use this to verify that everything is still in order.
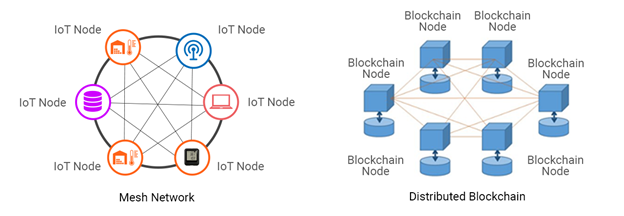
What Happens if a New Block is created?
If someone creates a new block, that new block is sent to everyone on the network. Each node then verifies the block to make sure that it hasn't tampered. If everything checks out each node adds this block to their own blockchain. All the nodes in this network create consensus.
They agree about which blocks are valid and which aren't. Blocks that are tampered with will be rejected by other nodes in the network. So, to successfully tamper a blockchain you'll need to tamper all blocks on the chain, redo the proof-of-work for each block and take control of more than 50% of the P2P(peer-to-peer) network. Only then will your tampered block become accepted by everyone else. This is almost impossible to do! Blockchains are also constantly evolving.
Incredible Benefits of Blockchain Across Industries
Healthcare: Using digital signatures on blockchain-based data that allows access only when authorized by multiple people could regulate the availability and maintain the privacy of health records. In addition, a community of people, including hospitals, doctors, patients, and insurance companies, could be part of the overall blockchain, reducing fraud in health-care payments.
Defense: Unauthorized access or modification of critical defense infrastructures, such as operating systems and network firmware, could seriously compromise national security. For most countries, defense infrastructure and computer systems are distributed across different locations. Blockchain technology distributed across multiple data centers can ensure security against attacks on important network and hardware equipment by ensuring consensus-based access for modification.
Government: Government departments that work in silos cause the exchange of information to be delayed, negatively impacting citizen services. Linking the data between the departments with blockchain ensures that data is released in the real-time when both the departments and the citizen consent to sharing data. Blockchain technology could improve transparency and check corruption in governments worldwide.
Conclusion
Blockchain has been both exciting and captivating to learn and research about a relatively novel technology. The blockchain continues to progress, it is noteworthy to keep a close watch on the blockchain, given its capabilities to innovate various areas that are relevant to the society as well as the day-to-day lives in the digital age. The blockchain address globalism with mobile applications and exchange platforms that facilitate financial and economic activities worldwide and it addresses democracy by reshaping the functions of governments, organizations, and corporations with commercial influence in addition to the blockchain's ability to make voting systems more effective.